Complete Guide to Self-Levelling Compound
Ensuring a surface that is impeccably smooth and level during a renovation project is paramount. Self-levelling compounds are indispensable for those who seek perfection in flooring. These compounds, a blend of cementitious materials and often polymers, are the preliminary layer in flooring, rendering uneven or rough surfaces perfectly smooth and flat.
Self-levelling compounds are specifically formulated to improve the flatness and uniformity of the substrate. This creates an ideal base for the final floor covering, be it tiles, carpet, or wood. This guide explores the facets of self-levelling compounds, including their composition, modes of application, and inherent advantages.
These compounds essentially synthesise cement, polymers, aggregates, and additives. Each plays a pivotal role in ensuring the compound’s performance, workability, and durability. Polymers augment the compound’s flexibility and adherence properties. On the other hand, the additives are integrated to modulate the flow, set time, and enhance other functional properties. The amalgamation of these components ensures that self-levelling compounds effectively rectify any substrate discrepancies, delivering a uniformly levelled surface ideal for any flooring type.
What is a self-levelling compound, and what is it composed of?
A self-levelling compound is a highly specialised, hybrid flooring solution primarily used to rectify and mitigate imperfections in the substrate, creating a smooth and level surface for subsequent floor installations. It is a fluid material that autonomously levels out, filling in depressions and eliminating protrusions. Hence, it is used extensively to correct surface irregularities like dips, bumps, or cracks on subfloors.
Detailed composition:
The composition of a self-levelling compound is predominantly comprised of the following components, each contributing to its unique properties:
- Cement: Acts as the foundational base of the compound, providing rigidity and structure.
- Polymers: These are incorporated to enhance the compound’s flexibility and adhesion, enabling it to bond efficiently with diverse substrates, accommodating minor movements and fluctuations in the substrate without compromising integrity.
- Additives: Specific additives are integrated to modulate and optimise the flow characteristics and setting time of the compound, ensuring a seamless, even spread over the substrate and aiding in the attainment of a flat, uniform surface.
- Aggregates: These are granular materials that provide bulk, stability, and structure to the compound, aiding in achieving the desired consistency and thickness.
- Pigments: Some compounds may contain pigments to impart colour to the compound, which could be advantageous in certain aesthetic or functional applications.
Upon application, the self-levelling compound spreads and levels itself out due to its low viscosity and optimised flow properties, filling in low spots and levelling high spots, thus creating a uniform, smooth surface. The refined balance of components in the compound ensures that it maintains its shape and structure once set, providing a stable and reliable base for subsequent floor coverings.
This foundational layer is pivotal for the longevity and quality of the overall flooring system. It rectifies substrate irregularities, preventing future issues such as cracking, debonding, or uneven wear in the final floor covering.
Types of self-levelling compounds
There are three major types of self-levelling compounds. Understanding their composition dictates their use. For example, residential properties and commercial spaces will have different requirements. However, the ultimate goal is to achieve dimensionally stable and level surfaces.
Water-based compounds
- Application: Ideal for residential and light commercial spaces due to their cost-effectiveness and ease of application.
- Characteristics: These are usually less viscous, user-friendly, and emit lower VOCs (Volatile Organic Compounds).
- Substrates: Suitable for concrete, wood, and other standard subfloor materials.
- Limitation: They might not be suitable for areas with heavy loads or extreme conditions due to lower strength and resistance.
Latex-based compounds
- Application: Preferred for surfaces prone to movement or vibration, such as wooden floors, due to their enhanced flexibility.
- Characteristics: They exhibit superior adhesion and flexibility, reducing the risk of cracking or debonding.
- Substrates: Ideal for substrates like wood, which may exhibit movement or dimensional instability.
- Curing: Latex-based compounds often require longer curing times compared to their counterparts.
Epoxy-based compounds
- Application: It is predominantly used in industrial settings where high strength and resistance to chemicals, impact, and abrasion are required.
- Characteristics: They are characterised by high compressive strength, chemical resistance, and durability.
- Substrates: Best suited for concrete and steel substrates in demanding industrial environments.
- Limitation: These compounds are more complex to mix and apply and are usually more expensive than water and latex-based compounds.
Polymer-modified compounds
- Application: Suitable for a wide range of applications with enhanced performance characteristics.
- Characteristics: They combine the properties of polymers and cementitious compounds for improved adhesion, flexibility, and water resistance.
- Substrates: Can be applied to various substrates, including concrete, wood, and tiles.
- Versatility: They can be customised with additives to achieve specific performance requirements.
Fast-setting compounds
- Application: Ideal for projects with tight timelines where rapid setting and curing are crucial.
- Characteristics: They offer quick drying times, allowing the progression to subsequent construction stages.
- Substrates: Suitable for most standard substrates, including concrete and wood.
- Consideration: The fast setting time requires a quick and efficient application to avoid premature drying and curing.
EWI Store’s products
| EWI-250 Self-Levelling Compound | ProLevel Fibre: Reinforced Flexible Floor Leveller |
| Internal Flooring | Internal Use |
| Manual or machine application | Manual application |
| Quick set in 2 hours | Set in 3 hours |
| Thickness – 2 to 100mm | Thickness 3 – 75mm |
| Basic surface levelling, including cement, concrete, load-bearing anhydrite screed, etc | Excellent flexibility for timber floors and underfloor heating systems |
| Tile after 8 hours | |
|
|
Application steps
1. Surface preparation
Before applying a self-levelling compound, it’s critical to prepare the substrate to ensure optimal adhesion and performance meticulously. Start by thoroughly cleaning the surface and removing any traces of dust, dirt, grease, oil, or loose and deteriorating materials. This step is imperative as contaminants left on the substrate can impede the compound’s adhesion, leading to future failures. Consider using a degreasing agent or an industrial cleaner for surfaces with stubborn contaminants like oil or grease.
Once the cleaning is complete, assess the substrate for any cracks, holes, or other damages and repair them using a suitable patching compound. After repairs, the application of a primer is crucial. A primer enhances the bond between the substrate and the levelling compound, preventing pinholing and bubble formation issues. Ensure that the chosen primer is compatible with the levelling compound and apply it per the manufacturer’s instructions, allowing adequate drying time before proceeding to the next step.
2. Mixing the compound
The mixing process is a pivotal step, and precision is key here. Accurate measurement of the compound and water (or any other recommended liquid) is essential. Follow the manufacturer’s specified ratio diligently to avoid inconsistencies in the mixture. Use a mechanical mixer to achieve a lump-free, homogenous consistency. Avoid overmixing as it could introduce air bubbles into the mix, leading to problems during application. Once mixed, the compound should be used immediately, considering its rapid-setting nature.
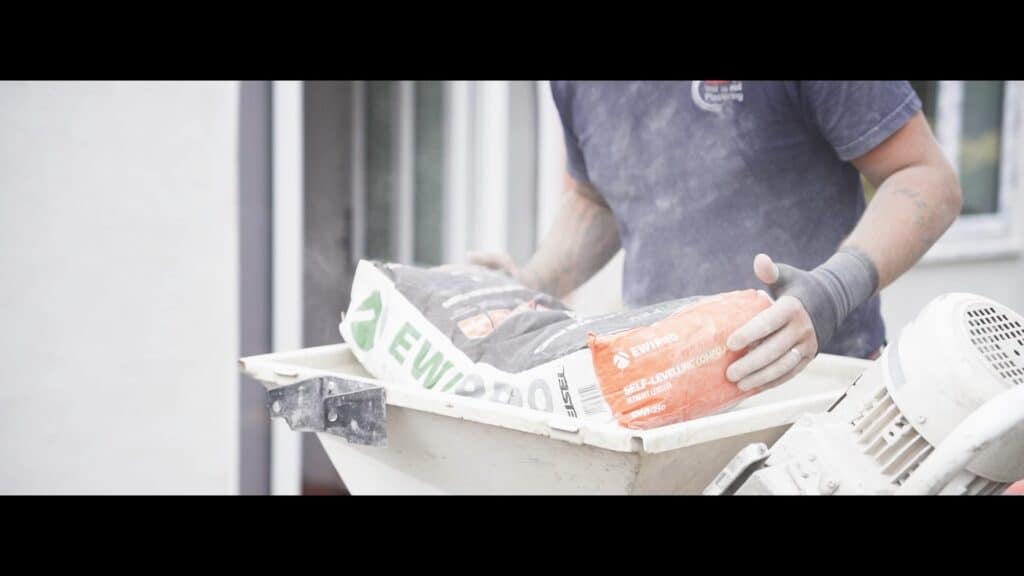

3. Application of the compound
Pour the mixed self-levelling compound strategically, starting from the furthest point of the room and working your way towards the exit. The compound should also be poured evenly over the surface, allowing it to flow and level out. Utilise a squeegee or a gauge rake to assist in spreading the compound to the desired thickness, ensuring it covers the entire area uniformly. Adhering to the manufacturer’s recommended application thickness is crucial to avoid cracking or insufficient coverage. A trowel can also be used to spread the compound manually for areas that are hard to reach or for detailing.
4. Curing process
After application, the self-levelling compound requires a sufficient curing period to achieve its full strength and properties. The drying time can vary depending on the type of compound used, ambient conditions like temperature and humidity, and the thickness of the application. Generally, it ranges between 1 to 3 days. During this period, it is paramount to avoid any traffic or disturbance to the area to prevent imperfections or damage to the freshly applied compound. Adhering to the manufacturer’s recommended drying time ensures the compound is adequately set before installing the final floor covering.
Advantages of self-levelling compounds
Uniform and smooth surface
One of the primary advantages of self-levelling compounds is their ability to provide a uniform and smooth surface, which is crucial for the optimal installation of final floor coverings. These compounds meticulously fill in the depressions and rectify undulations on the substrate, eliminating irregularities and imperfections. A smooth, flat surface is indispensable for the longevity and performance of floor coverings such as tiles, laminate, or carpet, ensuring they are laid evenly and securely.
Rapid application and setting
Applying self-levelling compounds is relatively swift and straightforward, significantly reducing downtime in construction or renovation projects. Many of these compounds are formulated to set and cure rapidly, allowing for the progression to subsequent stages of the flooring installation in a shorter timeframe. This setting is particularly advantageous in commercial settings, where minimising operational disruption is critical.
Enhanced durability and strength
Self-levelling compounds are imbued with properties that enhance the floor structure’s durability and strength. They are a robust intermediary layer between the substrate and the floor covering, distributing loads and stresses evenly across the surface. This uniform distribution of stresses mitigates the risk of cracking, deformation, and other structural damages to the floor covering, prolonging its lifespan and maintaining its aesthetic appeal over time.
Versatility and compatibility
Self-levelling compounds are versatile and compatible with various substrates, including concrete, wood, and tiles. This versatility is augmented by the availability of different compounds, each tailored to meet specific requirements and conditions of the project. Whether it’s a high-traffic industrial floor requiring chemical resistance or a residential space needing aesthetic appeal, there is a suitable self-levelling compound that can cater to diverse needs and preferences.
Accommodates varied floor coverings
The use of self-levelling compounds is not restrictive to specific floor coverings. Once cured, these compounds can accommodate varied floor coverings, including tiles, carpet, vinyl, and wood, providing ample flexibility in choosing the final floor’s desired aesthetic and functional attributes. Adapting to different floor coverings allows for greater design freedom and customisation, enabling the realisation of distinct architectural visions and preferences.
Things to consider
Substrate condition and preparation
Before applying a self-levelling compound, examining the substrate’s condition thoroughly is crucial. Any presence of contaminants, loose materials, or structural damage on the substrate can compromise the adhesion and performance of the compound. Proper preparation, including cleaning and repairing the substrate, is fundamental to achieving optimal results. Substrate moisture levels should also be evaluated, as excessive moisture can lead to failures such as debonding or blistering of the compound.
Material selection
Choosing the appropriate type of self-levelling compound is essential, considering the specific requirements and conditions of the project. Factors such as the substrate type, environmental conditions, desired drying time, and the intended floor covering should influence the selection. For instance, epoxy-based compounds may be more suited to industrial environments due to their enhanced strength and chemical resistance. In contrast, due to their flexibility, latex-based compounds might be preferable for surfaces prone to movement.
Manufacturer’s instructions
Adherence to the manufacturer’s instructions is paramount throughout the process, from mixing to application. Instructions typically include guidelines on the proper mixing ratios, drying times, and application thickness. However, deviations result in inconsistencies, poor performance, or failures of the compound. Reading and following the product datasheet and guidelines ensures the compound is prepared, applied, and cured correctly, optimising its performance and durability.
Ambient conditions
The environmental conditions during the application and curing of the self-levelling compound can significantly impact its performance. Temperature and humidity levels should be within the recommended range to prevent issues such as improper curing, cracking, or poor adhesion. Protecting the area from direct sunlight, wind, or precipitation is also essential, particularly for outdoor applications, to avoid rapid drying or contamination of the compound.
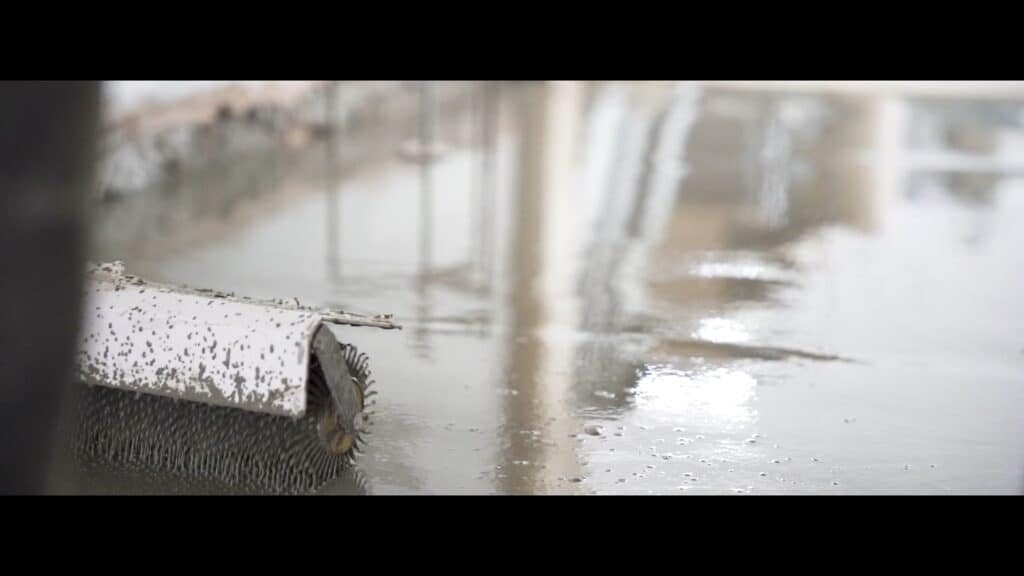

Budget and cost-effectiveness
Economic considerations should also influence decision-making. While self-levelling compounds are a valuable investment for achieving high-quality floors, balancing costs with project requirements and budget is essential. Opting for cost-effective solutions without compromising quality and performance is crucial. Therefore, exploring various products and their cost implications can help make informed, economically sound decisions.
Facebook
Twitter
LinkedIn
Your cart
Trade Account Login
We use cookies on our website to give you the most relevant experience by remembering your preferences and repeat visits. By clicking “Accept All”, you consent to the use of ALL the cookies. However, you may visit "Cookie Settings" to provide personalised consent.
Manage consent
Privacy Overview
This website uses cookies to improve your experience while you navigate through the website. Out of these, the cookies that are categorized as necessary are stored on your browser as they are essential for the working of basic functionalities of the website. We also use third-party cookies that help us analyze and understand how you use this website. These cookies will be stored in your browser only with your consent. You also have the option to opt-out of these cookies. But opting out of some of these cookies may affect your browsing experience.
Necessary cookies are absolutely essential for the website to function properly. These cookies ensure basic functionalities and security features of the website, anonymously.
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| __stripe_mid | 1 year | This cookie is set by Stripe payment gateway. This cookie is used to enable payment on the website without storing any patment information on a server. |
| __stripe_sid | 30 minutes | This cookie is set by Stripe payment gateway. This cookie is used to enable payment on the website without storing any patment information on a server. |
| _GRECAPTCHA | 5 months 27 days | This cookie is set by the Google recaptcha service to identify bots to protect the website against malicious spam attacks. |
| apbct_cookies_test | session | CleanTalk sets this cookie to prevent spam on comments and forms and act as a complete anti-spam solution and firewall for the site. |
| apbct_page_hits | session | CleanTalk sets this cookie to prevent spam on comments and forms and act as a complete anti-spam solution and firewall for the site. |
| apbct_prev_referer | session | Functional cookie placed by CleanTalk Spam Protect to store referring IDs and prevent unauthorized spam from being sent from the website. |
| apbct_site_landing_ts | session | CleanTalk sets this cookie to prevent spam on comments and forms and act as a complete anti-spam solution and firewall for the site. |
| apbct_site_referer | 3 days | This cookie is placed by CleanTalk Spam Protect to prevent spam and to store the referrer page address which led the user to the website. |
| apbct_timestamp | session | CleanTalk sets this cookie to prevent spam on comments and forms and act as a complete anti-spam solution and firewall for the site. |
| apbct_urls | 3 days | This cookie is placed by CleanTalk Spam Protect to prevent spam and to store the addresses (urls) visited on the website. |
| AWSALBCORS | 7 days | This cookie is managed by Amazon Web Services and is used for load balancing. |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-advertisement | 1 year | Set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin, this cookie is used to record the user consent for the cookies in the "Advertisement" category . |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-analytics | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Analytics". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-functional | 11 months | The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Functional". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-necessary | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookies is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Necessary". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-others | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Other. |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-performance | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Performance". |
| ct_checkjs | session | CleanTalk–Used to prevent spam on our comments and forms and acts as a complete anti-spam solution and firewall for this site. |
| ct_fkp_timestamp | session | CleanTalk sets this cookie to prevent spam on the site's comments/forms, and to act as a complete anti-spam solution and firewall for the site. |
| ct_pointer_data | session | CleanTalk sets this cookie to prevent spam on the site's comments/forms, and to act as a complete anti-spam solution and firewall for the site. |
| ct_ps_timestamp | session | CleanTalk sets this cookie to prevent spam on the site's comments/forms, and to act as a complete anti-spam solution and firewall for the site. |
| ct_sfw_pass_key | 1 month | CleanTalk sets this cookie to prevent spam on comments and forms and act as a complete anti-spam solution and firewall for the site. |
| ct_timezone | session | CleanTalk–Used to prevent spam on our comments and forms and acts as a complete anti-spam solution and firewall for this site. |
| elementor | never | This cookie is used by the website's WordPress theme. It allows the website owner to implement or change the website's content in real-time. |
| viewed_cookie_policy | 11 months | The cookie is set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin and is used to store whether or not user has consented to the use of cookies. It does not store any personal data. |
Functional cookies help to perform certain functionalities like sharing the content of the website on social media platforms, collect feedbacks, and other third-party features.
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| __zlcmid | 1 year | This cookie is used by Zendesk live chat and is used to store the live chat ID. |
| bcookie | 2 years | LinkedIn sets this cookie from LinkedIn share buttons and ad tags to recognize browser ID. |
| bscookie | 2 years | LinkedIn sets this cookie to store performed actions on the website. |
| lang | session | LinkedIn sets this cookie to remember a user's language setting. |
| lidc | 1 day | LinkedIn sets the lidc cookie to facilitate data center selection. |
| UserMatchHistory | 1 month | LinkedIn sets this cookie for LinkedIn Ads ID syncing. |
Performance cookies are used to understand and analyze the key performance indexes of the website which helps in delivering a better user experience for the visitors.
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| __utma | 2 years | This cookie is set by Google Analytics and is used to distinguish users and sessions. The cookie is created when the JavaScript library executes and there are no existing __utma cookies. The cookie is updated every time data is sent to Google Analytics. |
| __utmb | 30 minutes | Google Analytics sets this cookie, to determine new sessions/visits. __utmb cookie is created when the JavaScript library executes and there are no existing __utma cookies. It is updated every time data is sent to Google Analytics. |
| __utmc | session | The cookie is set by Google Analytics and is deleted when the user closes the browser. It is used to enable interoperability with urchin.js, which is an older version of Google Analytics and is used in conjunction with the __utmb cookie to determine new sessions/visits. |
| __utmt | 10 minutes | Google Analytics sets this cookie to inhibit request rate. |
| __utmv | 2 years | The __utmv cookie is set on the user's device, to enable Google Analytics to classify the visitor. |
| __utmz | 6 months | Google Analytics sets this cookie to store the traffic source or campaign by which the visitor reached the site. |
| sib_cuid | 6 months | Purechat uses this cookie to send data to purechat.com, to connect visitors to the reservation team and track visitors to stay on portal. |
| SRM_B | 1 year 24 days | Used by Microsoft Advertising as a unique ID for visitors. |
Analytical cookies are used to understand how visitors interact with the website. These cookies help provide information on metrics the number of visitors, bounce rate, traffic source, etc.
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| _ga | 2 years | The _ga cookie, installed by Google Analytics, calculates visitor, session and campaign data and also keeps track of site usage for the site's analytics report. The cookie stores information anonymously and assigns a randomly generated number to recognize unique visitors. |
| _gat_gtag_UA_61069204_2 | 1 minute | Set by Google to distinguish users. |
| _gat_UA-61069204-2 | 1 minute | A variation of the _gat cookie set by Google Analytics and Google Tag Manager to allow website owners to track visitor behaviour and measure site performance. The pattern element in the name contains the unique identity number of the account or website it relates to. |
| _gcl_au | 3 months | Provided by Google Tag Manager to experiment advertisement efficiency of websites using their services. |
| _gid | 1 day | Installed by Google Analytics, _gid cookie stores information on how visitors use a website, while also creating an analytics report of the website's performance. Some of the data that are collected include the number of visitors, their source, and the pages they visit anonymously. |
| _uetsid | 1 day | This cookies are used to collect analytical information about how visitors use the website. This information is used to compile report and improve site. |
| CONSENT | 2 years | YouTube sets this cookie via embedded youtube-videos and registers anonymous statistical data. |
Advertisement cookies are used to provide visitors with relevant ads and marketing campaigns. These cookies track visitors across websites and collect information to provide customized ads.
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| _fbp | 3 months | This cookie is set by Facebook to display advertisements when either on Facebook or on a digital platform powered by Facebook advertising, after visiting the website. |
| ANONCHK | 10 minutes | The ANONCHK cookie, set by Bing, is used to store a user's session ID and also verify the clicks from ads on the Bing search engine. The cookie helps in reporting and personalization as well. |
| fr | 3 months | Facebook sets this cookie to show relevant advertisements to users by tracking user behaviour across the web, on sites that have Facebook pixel or Facebook social plugin. |
| MUID | 1 year 24 days | Bing sets this cookie to recognize unique web browsers visiting Microsoft sites. This cookie is used for advertising, site analytics, and other operations. |
| NID | 6 months | NID cookie, set by Google, is used for advertising purposes; to limit the number of times the user sees an ad, to mute unwanted ads, and to measure the effectiveness of ads. |
| test_cookie | 15 minutes | The test_cookie is set by doubleclick.net and is used to determine if the user's browser supports cookies. |
| uuid | 6 months | MediaMath sets this cookie to avoid the same ads from being shown repeatedly and for relevant advertising. |
| VISITOR_INFO1_LIVE | 5 months 27 days | A cookie set by YouTube to measure bandwidth that determines whether the user gets the new or old player interface. |
| YSC | session | YSC cookie is set by Youtube and is used to track the views of embedded videos on Youtube pages. |
| yt-remote-connected-devices | never | YouTube sets this cookie to store the video preferences of the user using embedded YouTube video. |
| yt-remote-device-id | never | YouTube sets this cookie to store the video preferences of the user using embedded YouTube video. |
| yt.innertube::nextId | never | This cookie, set by YouTube, registers a unique ID to store data on what videos from YouTube the user has seen. |
| yt.innertube::requests | never | This cookie, set by YouTube, registers a unique ID to store data on what videos from YouTube the user has seen. |
Other uncategorized cookies are those that are being analyzed and have not been classified into a category as yet.
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| _clck | 1 year | No description |
| _clsk | 1 day | No description |
| _uetvid | 1 year 24 days | No description available. |
| AnalyticsSyncHistory | 1 month | No description |
| apbct_pixel_url | session | No description |
| apbct_visible_fields_0 | session | No description |
| apbct_visible_fields_1 | session | No description |
| apbct_visible_fields_10 | session | No description |
| apbct_visible_fields_2 | session | No description |
| apbct_visible_fields_3 | session | No description |
| apbct_visible_fields_4 | session | No description |
| apbct_visible_fields_5 | session | No description |
| apbct_visible_fields_6 | session | No description |
| apbct_visible_fields_7 | session | No description |
| apbct_visible_fields_8 | session | No description |
| apbct_visible_fields_9 | session | No description |
| ct_checked_emails | session | No description |
| ct_has_scrolled | session | No description |
| ct_mouse_moved | session | No description |
| ct_screen_info | session | No description |
| ictf_master | never | No description available. |
| li_gc | 2 years | No description |
| m | 2 years | No description available. |
| SM | session | No description available. |
| testinfinitycookie | session | No description |
| woocommerce_show_tax | 7 days | No description available. |
| wp_woocommerce_session_c5ac76b408021294cb56bcc27eddf8a1 | 2 days | No description |




2 thoughts on “Complete Guide to Self-Levelling Compound”
How do you get the air pockets out?
Hi Will, the best way to do this is to use a spiked aeration roller. It will disperse the compound and force the air pockets out, ensuring totally flat coverage.