4.8 out of 5 Stars on TrustPilot
How is EWI Made More Sustainable?
In recent years, the conversation around building practices has increasingly focused on sustainable building materials. One area where this shift is particularly notable is in the realm of external wall insulation (EWI). EWI plays a pivotal role in enhancing the energy efficiency of homes and buildings, but its sustainability quotient depends significantly on the materials used, the production processes, and the long-term impacts on the environment. In this blog, we’ll explore the strides being made in the EWI sector to promote sustainability.
Eco-friendly sustainable materials
Natural and renewable materials
Natural materials are at the forefront of the eco-friendly EWI movement. These materials are derived from renewable resources and have a significantly lower environmental impact compared to synthetic alternatives. Some of the key natural materials include:
- Wood Fibre: Derived from sustainably managed forests, wood fibre insulation is biodegradable and has a low embodied energy, meaning it requires less energy to produce. It also offers excellent thermal properties and can regulate indoor humidity levels, enhancing indoor air quality.
- Cork: Harvested from the bark of cork oak trees without harming the tree, cork is a renewable resource. Cork insulation panels are not only highly insulative but also naturally fire-resistant and durable. The production process of cork insulation is energy-efficient and generates almost no waste, as all parts of the bark are used.
- Hemp and Flax: These plant-based materials are gaining popularity for their low environmental impact and excellent insulation properties. Hemp and flax insulations are carbon-negative, meaning they absorb more carbon dioxide during their growth than is emitted during their processing.
Recycled materials
Using recycled materials in EWI helps reduce waste and the demand for virgin resources. Recycled materials can come from various sources and can be just as effective as new materials in terms of insulation performance.
- Recycled Plastic: Innovative companies are turning to recycled plastics to create insulation materials. These plastics are often sourced from consumer waste, such as PET bottles, and transformed into insulation boards or beads.
- Glass Wool: Made from recycled glass, glass wool is a common insulation material. The production process melts down the glass and spins it into fibres, creating an effective insulator with good thermal and sound insulation properties.
Low environmental impact on production
The sustainability of EWI materials also depends on the environmental impact of their production process. Eco-friendly materials are typically those that require less energy to manufacture and result in lower emissions. For instance, materials that are locally sourced reduce transportation emissions, and those produced using renewable energy further reduce their carbon footprint.
Eco-friendly EWI materials should not only be in their production but also in their performance. Materials that offer high durability and require less maintenance contribute to sustainability by reducing the need for replacements and repairs over time. Moreover, materials that enhance energy efficiency in buildings lower the overall carbon footprint of the structures they insulate.
Recycling and reusing
Recycled materials
- Reduction in Landfill Waste: By using recycled materials in EWI, we can significantly reduce the amount of waste sent to landfills. Construction and demolition waste constitutes a large percentage of total landfill waste, and recycling materials for EWI can help mitigate this.
- Lower Carbon Footprint: The process of recycling materials for EWI usually consumes less energy compared to manufacturing new insulation materials. This reduced energy expenditure translates into a lower carbon footprint for the insulation products.
- Conservation of Resources: Recycling helps in conserving natural resources. For instance, using recycled glass or plastic reduces the need for new raw materials, thus preserving natural resources and reducing the environmental impact associated with their extraction and processing.
Examples
- Recycled Glass Wool: Glass wool, often used in EWI, can be made from recycled glass bottles. The recycled glass is melted and spun into a fibrous insulation material, which provides excellent thermal properties.
- Expanded Polystyrene (EPS) with Recycled Content: EPS, commonly used in EWI systems, can include recycled polystyrene. Manufacturers are increasingly incorporating recycled EPS into new products, thereby reducing the reliance on virgin materials.
- Recycled Plastic Insulation Boards: Some insulation boards are now being manufactured using recycled plastics. These boards are not only environmentally friendly but also provide effective insulation and are often water-resistant and durable.
The role of reusing materials in EWI
- Upcycling EWI Materials: Upcycling involves repurposing materials for a use that is of higher value than the original. In EWI, this could involve using discarded materials, like wood offcuts or recycled cotton, in insulation products.
- Modular and Reusable EWI Systems: Some EWI systems are designed to be modular, allowing for components to be easily disassembled and reused in different buildings or settings. This approach extends the life of the materials and reduces waste.
- Refurbishing EWI Materials: In some cases, EWI materials removed from buildings can be refurbished or reconditioned for reuse. This process often involves cleaning, repairing, or reprocessing materials to ensure they meet the necessary standards for insulation performance.
Despite the benefits, there are challenges in recycling and reusing materials for EWI. These include ensuring the quality and safety of recycled materials and overcoming logistical hurdles in collecting and processing used materials. However, as technology advances and awareness increases, the potential for recycling and reusing materials in EWI is expected to grow. Innovations in material processing and a stronger emphasis on circular economy principles in the construction sector are paving the way for more sustainable EWI solutions.
Reducing carbon footprint
Energy-efficient manufacturing processes
- Optimising Production Line Efficiency: Manufacturers are increasingly adopting energy-efficient technologies in their production lines. This includes using advanced machinery that requires less energy to operate and implementing process improvements that minimize energy waste.
- Heat Recovery Systems: Many insulation materials require high-temperature processes. By installing heat recovery systems, manufacturers can capture and reuse heat that would otherwise be wasted, significantly reducing energy consumption.
Use of renewable energy sources
- Solar and Wind Power: More factories are transitioning to renewable energy sources like solar and wind power for their energy needs. This shift not only reduces carbon emissions but also lessens the dependency on fossil fuels.
- Biomass Energy: In some cases, manufacturers are using biomass boilers, which burn organic waste materials, to generate energy for production processes. Biomass is considered a renewable source of energy and can help reduce carbon emissions compared to traditional fossil fuels.
Sustainable material sourcing
- Locally Sourced Materials: Using locally sourced materials can significantly reduce the carbon footprint associated with transportation. Manufacturers are increasingly favouring local suppliers, which also supports local economies.
- Sustainable Raw Material Selection: Choosing raw materials that are sustainably harvested or produced can greatly reduce the environmental impact. For example, using wood from responsibly managed forests or recycled materials lessens the depletion of natural resources.
Reducing waste and improving material efficiency
- Recycling Production Waste: Many manufacturers are now recycling waste generated during the production process. This not only reduces the amount of waste sent to landfills but also conserves resources by reusing materials.
- Lean Manufacturing Principles: Implementing lean manufacturing principles helps in minimizing waste during production. This includes optimizing material usage and reducing excess inventory, leading to a more efficient and eco-friendly manufacturing process.
Transportation and logistics
- Efficient Distribution Networks: Optimizing transportation routes and logistics can significantly lower the carbon emissions associated with delivering EWI products to the market. This includes using fuel-efficient vehicles and consolidating shipments to minimize trips.
- Electric and Low-Emission Vehicles: Some manufacturers are investing in electric or low-emission vehicles for transportation needs, further reducing their carbon footprint.
Enhancing durability and performance
Sustainability is not just about the materials and production processes; it’s also about the longevity and performance of the EWI. Durable materials that don’t require frequent replacement reduce waste and the need for additional resources over time. Furthermore, advanced EWI systems that offer better thermal performance contribute to reducing energy consumption in buildings, which is a significant factor in their overall environmental impact.
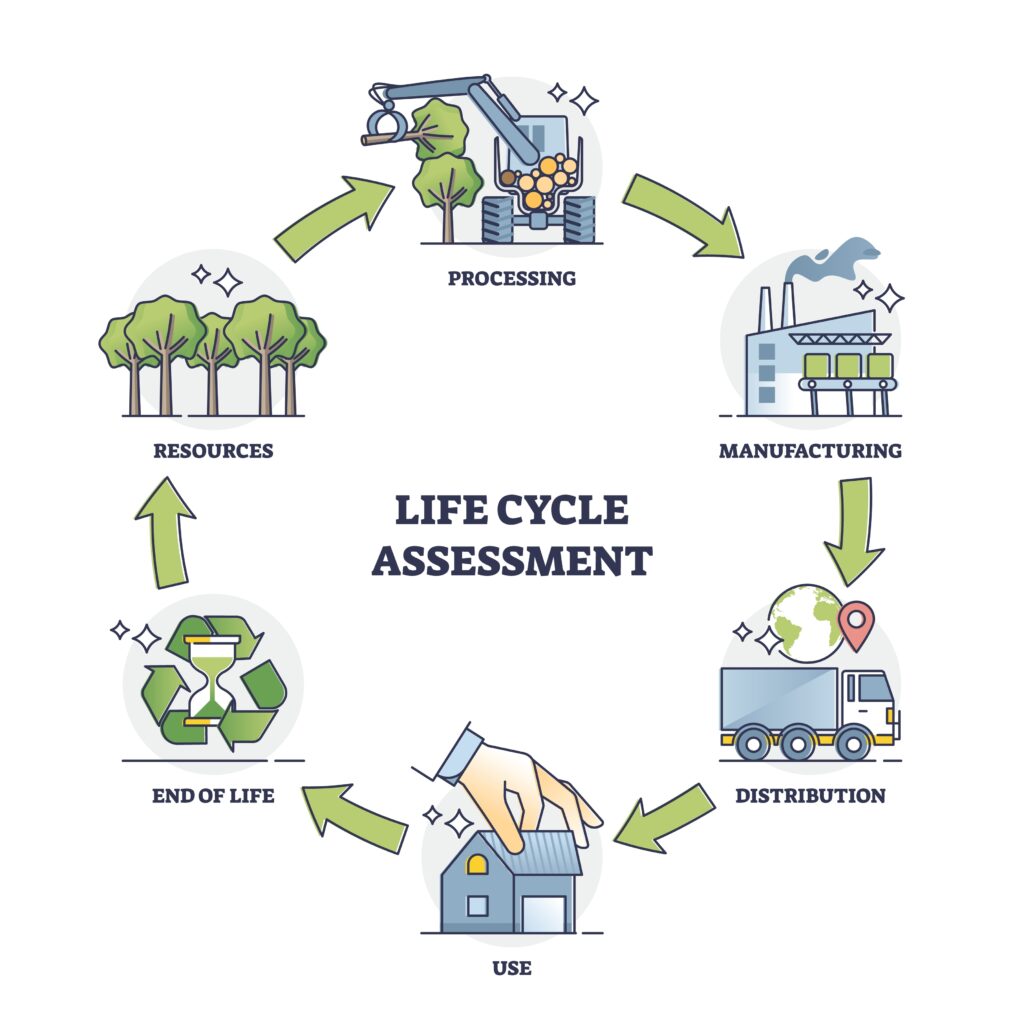
Life Cycle Assessment and sustainability
A comprehensive approach to sustainability involves evaluating the entire life cycle of EWI products. This means examining the environmental impact from the extraction of raw materials to the production process, transportation, installation, lifespan, and eventual disposal or recycling. A life cycle assessment helps in understanding the overall environmental footprint and in making informed decisions to reduce it.
Promoting green building certifications
EWI plays a vital role in helping buildings achieve green certifications like LEED or BREEAM. These certifications have stringent criteria for energy efficiency and environmental impact, and sustainable EWI systems can contribute significantly to meeting these standards.
Facebook
Twitter
LinkedIn
Your cart
Trade Account Login
We use cookies on our website to give you the most relevant experience by remembering your preferences and repeat visits. By clicking “Accept All”, you consent to the use of ALL the cookies. However, you may visit "Cookie Settings" to provide personalised consent.
Manage consent
Privacy Overview
This website uses cookies to improve your experience while you navigate through the website. Out of these, the cookies that are categorized as necessary are stored on your browser as they are essential for the working of basic functionalities of the website. We also use third-party cookies that help us analyze and understand how you use this website. These cookies will be stored in your browser only with your consent. You also have the option to opt-out of these cookies. But opting out of some of these cookies may affect your browsing experience.
Necessary cookies are absolutely essential for the website to function properly. These cookies ensure basic functionalities and security features of the website, anonymously.
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| __stripe_mid | 1 year | This cookie is set by Stripe payment gateway. This cookie is used to enable payment on the website without storing any patment information on a server. |
| __stripe_sid | 30 minutes | This cookie is set by Stripe payment gateway. This cookie is used to enable payment on the website without storing any patment information on a server. |
| _GRECAPTCHA | 5 months 27 days | This cookie is set by the Google recaptcha service to identify bots to protect the website against malicious spam attacks. |
| apbct_cookies_test | session | CleanTalk sets this cookie to prevent spam on comments and forms and act as a complete anti-spam solution and firewall for the site. |
| apbct_page_hits | session | CleanTalk sets this cookie to prevent spam on comments and forms and act as a complete anti-spam solution and firewall for the site. |
| apbct_prev_referer | session | Functional cookie placed by CleanTalk Spam Protect to store referring IDs and prevent unauthorized spam from being sent from the website. |
| apbct_site_landing_ts | session | CleanTalk sets this cookie to prevent spam on comments and forms and act as a complete anti-spam solution and firewall for the site. |
| apbct_site_referer | 3 days | This cookie is placed by CleanTalk Spam Protect to prevent spam and to store the referrer page address which led the user to the website. |
| apbct_timestamp | session | CleanTalk sets this cookie to prevent spam on comments and forms and act as a complete anti-spam solution and firewall for the site. |
| apbct_urls | 3 days | This cookie is placed by CleanTalk Spam Protect to prevent spam and to store the addresses (urls) visited on the website. |
| AWSALBCORS | 7 days | This cookie is managed by Amazon Web Services and is used for load balancing. |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-advertisement | 1 year | Set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin, this cookie is used to record the user consent for the cookies in the "Advertisement" category . |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-analytics | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Analytics". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-functional | 11 months | The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Functional". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-necessary | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookies is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Necessary". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-others | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Other. |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-performance | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Performance". |
| ct_checkjs | session | CleanTalk–Used to prevent spam on our comments and forms and acts as a complete anti-spam solution and firewall for this site. |
| ct_fkp_timestamp | session | CleanTalk sets this cookie to prevent spam on the site's comments/forms, and to act as a complete anti-spam solution and firewall for the site. |
| ct_pointer_data | session | CleanTalk sets this cookie to prevent spam on the site's comments/forms, and to act as a complete anti-spam solution and firewall for the site. |
| ct_ps_timestamp | session | CleanTalk sets this cookie to prevent spam on the site's comments/forms, and to act as a complete anti-spam solution and firewall for the site. |
| ct_sfw_pass_key | 1 month | CleanTalk sets this cookie to prevent spam on comments and forms and act as a complete anti-spam solution and firewall for the site. |
| ct_timezone | session | CleanTalk–Used to prevent spam on our comments and forms and acts as a complete anti-spam solution and firewall for this site. |
| elementor | never | This cookie is used by the website's WordPress theme. It allows the website owner to implement or change the website's content in real-time. |
| viewed_cookie_policy | 11 months | The cookie is set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin and is used to store whether or not user has consented to the use of cookies. It does not store any personal data. |
Functional cookies help to perform certain functionalities like sharing the content of the website on social media platforms, collect feedbacks, and other third-party features.
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| __zlcmid | 1 year | This cookie is used by Zendesk live chat and is used to store the live chat ID. |
| bcookie | 2 years | LinkedIn sets this cookie from LinkedIn share buttons and ad tags to recognize browser ID. |
| bscookie | 2 years | LinkedIn sets this cookie to store performed actions on the website. |
| lang | session | LinkedIn sets this cookie to remember a user's language setting. |
| lidc | 1 day | LinkedIn sets the lidc cookie to facilitate data center selection. |
| UserMatchHistory | 1 month | LinkedIn sets this cookie for LinkedIn Ads ID syncing. |
Performance cookies are used to understand and analyze the key performance indexes of the website which helps in delivering a better user experience for the visitors.
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| __utma | 2 years | This cookie is set by Google Analytics and is used to distinguish users and sessions. The cookie is created when the JavaScript library executes and there are no existing __utma cookies. The cookie is updated every time data is sent to Google Analytics. |
| __utmb | 30 minutes | Google Analytics sets this cookie, to determine new sessions/visits. __utmb cookie is created when the JavaScript library executes and there are no existing __utma cookies. It is updated every time data is sent to Google Analytics. |
| __utmc | session | The cookie is set by Google Analytics and is deleted when the user closes the browser. It is used to enable interoperability with urchin.js, which is an older version of Google Analytics and is used in conjunction with the __utmb cookie to determine new sessions/visits. |
| __utmt | 10 minutes | Google Analytics sets this cookie to inhibit request rate. |
| __utmv | 2 years | The __utmv cookie is set on the user's device, to enable Google Analytics to classify the visitor. |
| __utmz | 6 months | Google Analytics sets this cookie to store the traffic source or campaign by which the visitor reached the site. |
| sib_cuid | 6 months | Purechat uses this cookie to send data to purechat.com, to connect visitors to the reservation team and track visitors to stay on portal. |
| SRM_B | 1 year 24 days | Used by Microsoft Advertising as a unique ID for visitors. |
Analytical cookies are used to understand how visitors interact with the website. These cookies help provide information on metrics the number of visitors, bounce rate, traffic source, etc.
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| _ga | 2 years | The _ga cookie, installed by Google Analytics, calculates visitor, session and campaign data and also keeps track of site usage for the site's analytics report. The cookie stores information anonymously and assigns a randomly generated number to recognize unique visitors. |
| _gat_gtag_UA_61069204_2 | 1 minute | Set by Google to distinguish users. |
| _gat_UA-61069204-2 | 1 minute | A variation of the _gat cookie set by Google Analytics and Google Tag Manager to allow website owners to track visitor behaviour and measure site performance. The pattern element in the name contains the unique identity number of the account or website it relates to. |
| _gcl_au | 3 months | Provided by Google Tag Manager to experiment advertisement efficiency of websites using their services. |
| _gid | 1 day | Installed by Google Analytics, _gid cookie stores information on how visitors use a website, while also creating an analytics report of the website's performance. Some of the data that are collected include the number of visitors, their source, and the pages they visit anonymously. |
| _uetsid | 1 day | This cookies are used to collect analytical information about how visitors use the website. This information is used to compile report and improve site. |
| CONSENT | 2 years | YouTube sets this cookie via embedded youtube-videos and registers anonymous statistical data. |
Advertisement cookies are used to provide visitors with relevant ads and marketing campaigns. These cookies track visitors across websites and collect information to provide customized ads.
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| _fbp | 3 months | This cookie is set by Facebook to display advertisements when either on Facebook or on a digital platform powered by Facebook advertising, after visiting the website. |
| ANONCHK | 10 minutes | The ANONCHK cookie, set by Bing, is used to store a user's session ID and also verify the clicks from ads on the Bing search engine. The cookie helps in reporting and personalization as well. |
| fr | 3 months | Facebook sets this cookie to show relevant advertisements to users by tracking user behaviour across the web, on sites that have Facebook pixel or Facebook social plugin. |
| MUID | 1 year 24 days | Bing sets this cookie to recognize unique web browsers visiting Microsoft sites. This cookie is used for advertising, site analytics, and other operations. |
| NID | 6 months | NID cookie, set by Google, is used for advertising purposes; to limit the number of times the user sees an ad, to mute unwanted ads, and to measure the effectiveness of ads. |
| test_cookie | 15 minutes | The test_cookie is set by doubleclick.net and is used to determine if the user's browser supports cookies. |
| uuid | 6 months | MediaMath sets this cookie to avoid the same ads from being shown repeatedly and for relevant advertising. |
| VISITOR_INFO1_LIVE | 5 months 27 days | A cookie set by YouTube to measure bandwidth that determines whether the user gets the new or old player interface. |
| YSC | session | YSC cookie is set by Youtube and is used to track the views of embedded videos on Youtube pages. |
| yt-remote-connected-devices | never | YouTube sets this cookie to store the video preferences of the user using embedded YouTube video. |
| yt-remote-device-id | never | YouTube sets this cookie to store the video preferences of the user using embedded YouTube video. |
| yt.innertube::nextId | never | This cookie, set by YouTube, registers a unique ID to store data on what videos from YouTube the user has seen. |
| yt.innertube::requests | never | This cookie, set by YouTube, registers a unique ID to store data on what videos from YouTube the user has seen. |
Other uncategorized cookies are those that are being analyzed and have not been classified into a category as yet.
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| _clck | 1 year | No description |
| _clsk | 1 day | No description |
| _uetvid | 1 year 24 days | No description available. |
| AnalyticsSyncHistory | 1 month | No description |
| apbct_pixel_url | session | No description |
| apbct_visible_fields_0 | session | No description |
| apbct_visible_fields_1 | session | No description |
| apbct_visible_fields_10 | session | No description |
| apbct_visible_fields_2 | session | No description |
| apbct_visible_fields_3 | session | No description |
| apbct_visible_fields_4 | session | No description |
| apbct_visible_fields_5 | session | No description |
| apbct_visible_fields_6 | session | No description |
| apbct_visible_fields_7 | session | No description |
| apbct_visible_fields_8 | session | No description |
| apbct_visible_fields_9 | session | No description |
| ct_checked_emails | session | No description |
| ct_has_scrolled | session | No description |
| ct_mouse_moved | session | No description |
| ct_screen_info | session | No description |
| ictf_master | never | No description available. |
| li_gc | 2 years | No description |
| m | 2 years | No description available. |
| SM | session | No description available. |
| testinfinitycookie | session | No description |
| woocommerce_show_tax | 7 days | No description available. |
| wp_woocommerce_session_c5ac76b408021294cb56bcc27eddf8a1 | 2 days | No description |


2 thoughts on “How is EWI Made More Sustainable?”
What’s LEED and BREEAM?
Hi Jack, these are energy efficiency certificates.
LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) is a globally recognised green building certification system. It provides a framework for environmentally responsible and resource-efficient building design, construction, operation, and maintenance. Buildings are assessed across several categories such as energy efficiency, water usage, and air quality, and are then awarded certification levels like Certified, Silver, Gold, or Platinum based on their performance.
BREEAM (Building Research Establishment Environmental Assessment Method), originating in the UK, is one of the world’s foremost environmental assessment methods for buildings. It evaluates the sustainability of buildings across multiple categories, including energy, health and wellbeing, pollution, transport, and materials. BREEAM certification levels, ranging from Pass to Outstanding, indicate the performance of a building in terms of its environmental, social, and economic sustainability.