4.8 out of 5 Stars on TrustPilot
Thermal Bridges
Thermal bridges are very common in old houses or houses with insufficient insulation. Thermal bridges cause the affected part of the construction to have a significantly higher heat transfer than the surrounding materials. This results in an overall reduction in the thermal performance of the construction. Partially insulated building elements are responsible for up to 35% of thermal losses and increased condensation that leads to mould growth.
Thermal Bridges: 3 Types
Thermal bridges can be classified into three main types (Leeds Beckett University: Low Carbon Housing Learning Zone):
- Repeating or quasi-homogeneous thermal bridges usually follow a regular pattern and are evenly distributed over an area of the thermal envelope
- Non-repeating or linear thermal bridges are often caused by discontinuities in the thermal envelope and occur at a specific point in the construction
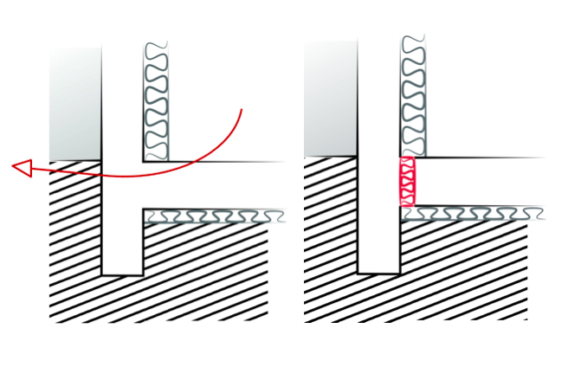
- Geometrical thermal bridges are a result of the geometry or shape of the thermal envelope
The most common parts of construction where the thermal bridges can occur are:
- The parts of the building envelope that are exposed to the external environment and have a different thermal conductivity
- The parts where a change in the thickness of the fabric occurs
- The wall-floor-ceiling junctions of the building where there is a difference between internal and external areas
To avoid thermal bridging you should ensure that your house is properly insulated in the affected areas:
- Concrete balconies that extend the floor slab through the building envelope.
- Areas around glazing, window frames and rooflights
- Metal ties in masonry cavity external walls
- Ceiling joists in cold pitched roofs
- Ground floor joists in an insulated suspended timber ground floor
- Timber studwork and I-beams in timber frame constructions
- Mortar joints in an insulating block inner leaf
- Areas round loft hatches
- Wall/ roof junctions or wall/ floor junctions
- At the corner of an external wall
- Junctions between adjacent walls
Strategies For Avoiding Thermal Bridges:
- Apply a continuous layer of insulation (such as EPS or Mineral Wool around the external walls of your house
- Install insulation at the outside corner of your building where the walls and floor are connected
By reducing thermal bridges you will have saved a great amount of heat losses and energy needs of your home resulting in reduced energy bills and increased building lifespan.
Facebook
Twitter
LinkedIn
Your cart
Trade Account Login
We use cookies on our website to give you the most relevant experience by remembering your preferences and repeat visits. By clicking “Accept All”, you consent to the use of ALL the cookies. However, you may visit "Cookie Settings" to provide personalised consent.
Manage consent
Privacy Overview
This website uses cookies to improve your experience while you navigate through the website. Out of these, the cookies that are categorized as necessary are stored on your browser as they are essential for the working of basic functionalities of the website. We also use third-party cookies that help us analyze and understand how you use this website. These cookies will be stored in your browser only with your consent. You also have the option to opt-out of these cookies. But opting out of some of these cookies may affect your browsing experience.
Necessary cookies are absolutely essential for the website to function properly. These cookies ensure basic functionalities and security features of the website, anonymously.
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| __stripe_mid | 1 year | This cookie is set by Stripe payment gateway. This cookie is used to enable payment on the website without storing any patment information on a server. |
| __stripe_sid | 30 minutes | This cookie is set by Stripe payment gateway. This cookie is used to enable payment on the website without storing any patment information on a server. |
| _GRECAPTCHA | 5 months 27 days | This cookie is set by the Google recaptcha service to identify bots to protect the website against malicious spam attacks. |
| apbct_cookies_test | session | CleanTalk sets this cookie to prevent spam on comments and forms and act as a complete anti-spam solution and firewall for the site. |
| apbct_page_hits | session | CleanTalk sets this cookie to prevent spam on comments and forms and act as a complete anti-spam solution and firewall for the site. |
| apbct_prev_referer | session | Functional cookie placed by CleanTalk Spam Protect to store referring IDs and prevent unauthorized spam from being sent from the website. |
| apbct_site_landing_ts | session | CleanTalk sets this cookie to prevent spam on comments and forms and act as a complete anti-spam solution and firewall for the site. |
| apbct_site_referer | 3 days | This cookie is placed by CleanTalk Spam Protect to prevent spam and to store the referrer page address which led the user to the website. |
| apbct_timestamp | session | CleanTalk sets this cookie to prevent spam on comments and forms and act as a complete anti-spam solution and firewall for the site. |
| apbct_urls | 3 days | This cookie is placed by CleanTalk Spam Protect to prevent spam and to store the addresses (urls) visited on the website. |
| AWSALBCORS | 7 days | This cookie is managed by Amazon Web Services and is used for load balancing. |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-advertisement | 1 year | Set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin, this cookie is used to record the user consent for the cookies in the "Advertisement" category . |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-analytics | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Analytics". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-functional | 11 months | The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Functional". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-necessary | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookies is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Necessary". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-others | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Other. |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-performance | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Performance". |
| ct_checkjs | session | CleanTalk–Used to prevent spam on our comments and forms and acts as a complete anti-spam solution and firewall for this site. |
| ct_fkp_timestamp | session | CleanTalk sets this cookie to prevent spam on the site's comments/forms, and to act as a complete anti-spam solution and firewall for the site. |
| ct_pointer_data | session | CleanTalk sets this cookie to prevent spam on the site's comments/forms, and to act as a complete anti-spam solution and firewall for the site. |
| ct_ps_timestamp | session | CleanTalk sets this cookie to prevent spam on the site's comments/forms, and to act as a complete anti-spam solution and firewall for the site. |
| ct_sfw_pass_key | 1 month | CleanTalk sets this cookie to prevent spam on comments and forms and act as a complete anti-spam solution and firewall for the site. |
| ct_timezone | session | CleanTalk–Used to prevent spam on our comments and forms and acts as a complete anti-spam solution and firewall for this site. |
| elementor | never | This cookie is used by the website's WordPress theme. It allows the website owner to implement or change the website's content in real-time. |
| viewed_cookie_policy | 11 months | The cookie is set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin and is used to store whether or not user has consented to the use of cookies. It does not store any personal data. |
Functional cookies help to perform certain functionalities like sharing the content of the website on social media platforms, collect feedbacks, and other third-party features.
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| __zlcmid | 1 year | This cookie is used by Zendesk live chat and is used to store the live chat ID. |
| bcookie | 2 years | LinkedIn sets this cookie from LinkedIn share buttons and ad tags to recognize browser ID. |
| bscookie | 2 years | LinkedIn sets this cookie to store performed actions on the website. |
| lang | session | LinkedIn sets this cookie to remember a user's language setting. |
| lidc | 1 day | LinkedIn sets the lidc cookie to facilitate data center selection. |
| UserMatchHistory | 1 month | LinkedIn sets this cookie for LinkedIn Ads ID syncing. |
Performance cookies are used to understand and analyze the key performance indexes of the website which helps in delivering a better user experience for the visitors.
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| __utma | 2 years | This cookie is set by Google Analytics and is used to distinguish users and sessions. The cookie is created when the JavaScript library executes and there are no existing __utma cookies. The cookie is updated every time data is sent to Google Analytics. |
| __utmb | 30 minutes | Google Analytics sets this cookie, to determine new sessions/visits. __utmb cookie is created when the JavaScript library executes and there are no existing __utma cookies. It is updated every time data is sent to Google Analytics. |
| __utmc | session | The cookie is set by Google Analytics and is deleted when the user closes the browser. It is used to enable interoperability with urchin.js, which is an older version of Google Analytics and is used in conjunction with the __utmb cookie to determine new sessions/visits. |
| __utmt | 10 minutes | Google Analytics sets this cookie to inhibit request rate. |
| __utmv | 2 years | The __utmv cookie is set on the user's device, to enable Google Analytics to classify the visitor. |
| __utmz | 6 months | Google Analytics sets this cookie to store the traffic source or campaign by which the visitor reached the site. |
| sib_cuid | 6 months | Purechat uses this cookie to send data to purechat.com, to connect visitors to the reservation team and track visitors to stay on portal. |
| SRM_B | 1 year 24 days | Used by Microsoft Advertising as a unique ID for visitors. |
Analytical cookies are used to understand how visitors interact with the website. These cookies help provide information on metrics the number of visitors, bounce rate, traffic source, etc.
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| _ga | 2 years | The _ga cookie, installed by Google Analytics, calculates visitor, session and campaign data and also keeps track of site usage for the site's analytics report. The cookie stores information anonymously and assigns a randomly generated number to recognize unique visitors. |
| _gat_gtag_UA_61069204_2 | 1 minute | Set by Google to distinguish users. |
| _gat_UA-61069204-2 | 1 minute | A variation of the _gat cookie set by Google Analytics and Google Tag Manager to allow website owners to track visitor behaviour and measure site performance. The pattern element in the name contains the unique identity number of the account or website it relates to. |
| _gcl_au | 3 months | Provided by Google Tag Manager to experiment advertisement efficiency of websites using their services. |
| _gid | 1 day | Installed by Google Analytics, _gid cookie stores information on how visitors use a website, while also creating an analytics report of the website's performance. Some of the data that are collected include the number of visitors, their source, and the pages they visit anonymously. |
| _uetsid | 1 day | This cookies are used to collect analytical information about how visitors use the website. This information is used to compile report and improve site. |
| CONSENT | 2 years | YouTube sets this cookie via embedded youtube-videos and registers anonymous statistical data. |
Advertisement cookies are used to provide visitors with relevant ads and marketing campaigns. These cookies track visitors across websites and collect information to provide customized ads.
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| _fbp | 3 months | This cookie is set by Facebook to display advertisements when either on Facebook or on a digital platform powered by Facebook advertising, after visiting the website. |
| ANONCHK | 10 minutes | The ANONCHK cookie, set by Bing, is used to store a user's session ID and also verify the clicks from ads on the Bing search engine. The cookie helps in reporting and personalization as well. |
| fr | 3 months | Facebook sets this cookie to show relevant advertisements to users by tracking user behaviour across the web, on sites that have Facebook pixel or Facebook social plugin. |
| MUID | 1 year 24 days | Bing sets this cookie to recognize unique web browsers visiting Microsoft sites. This cookie is used for advertising, site analytics, and other operations. |
| NID | 6 months | NID cookie, set by Google, is used for advertising purposes; to limit the number of times the user sees an ad, to mute unwanted ads, and to measure the effectiveness of ads. |
| test_cookie | 15 minutes | The test_cookie is set by doubleclick.net and is used to determine if the user's browser supports cookies. |
| uuid | 6 months | MediaMath sets this cookie to avoid the same ads from being shown repeatedly and for relevant advertising. |
| VISITOR_INFO1_LIVE | 5 months 27 days | A cookie set by YouTube to measure bandwidth that determines whether the user gets the new or old player interface. |
| YSC | session | YSC cookie is set by Youtube and is used to track the views of embedded videos on Youtube pages. |
| yt-remote-connected-devices | never | YouTube sets this cookie to store the video preferences of the user using embedded YouTube video. |
| yt-remote-device-id | never | YouTube sets this cookie to store the video preferences of the user using embedded YouTube video. |
| yt.innertube::nextId | never | This cookie, set by YouTube, registers a unique ID to store data on what videos from YouTube the user has seen. |
| yt.innertube::requests | never | This cookie, set by YouTube, registers a unique ID to store data on what videos from YouTube the user has seen. |
Other uncategorized cookies are those that are being analyzed and have not been classified into a category as yet.
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| _clck | 1 year | No description |
| _clsk | 1 day | No description |
| _uetvid | 1 year 24 days | No description available. |
| AnalyticsSyncHistory | 1 month | No description |
| apbct_pixel_url | session | No description |
| apbct_visible_fields_0 | session | No description |
| apbct_visible_fields_1 | session | No description |
| apbct_visible_fields_10 | session | No description |
| apbct_visible_fields_2 | session | No description |
| apbct_visible_fields_3 | session | No description |
| apbct_visible_fields_4 | session | No description |
| apbct_visible_fields_5 | session | No description |
| apbct_visible_fields_6 | session | No description |
| apbct_visible_fields_7 | session | No description |
| apbct_visible_fields_8 | session | No description |
| apbct_visible_fields_9 | session | No description |
| ct_checked_emails | session | No description |
| ct_has_scrolled | session | No description |
| ct_mouse_moved | session | No description |
| ct_screen_info | session | No description |
| ictf_master | never | No description available. |
| li_gc | 2 years | No description |
| m | 2 years | No description available. |
| SM | session | No description available. |
| testinfinitycookie | session | No description |
| woocommerce_show_tax | 7 days | No description available. |
| wp_woocommerce_session_c5ac76b408021294cb56bcc27eddf8a1 | 2 days | No description |



6 thoughts on “Thermal Bridges”
Ok thanks for posting. Do you have a manual on how to avoid thermal bridging at the parapet? We are looking to insulate the walls of the back of the house, but the roof is near flat, so I would like to understand how it can be finished off at the top.
Hi Simon there are ways to do this to minimise cold bridging but some of the options could be quite expensive. For example you can use coping stones or you can extend the roof profile so the insulation buts up against the roof line.
If you go to the EWI Pro system designer website they will have more information on this subject.
I have had external wall insulation installed and have noticed mould form on top of the back bedroom wall – the insulation I belive is on the other side. Has anyone else experienced this? I spoke to the installer and he said it could be something to do with the loft insulation I also had installed. Any help, much appreciated.
How can I prevent cold bridging if I need to put a screw into a wall – does the rawlplug prevent cold bridging occurring or are there special plugs that prevent this from occurring. Thoughts would be useful as we have just had cavity wall insulation injected into our cavity and I need to put up a washing line, but don’t want to get condensation forming on the inside wall where a new cold spot appears because of the cold bridging.
Thermal bridging is critically important. I am glad you are making people aware of it.
Do thermal bridges honestly matter? Seems OTT to me.