
- Ventilation strategies
- Mechanical ventilation systems
- Smart ventilation controls
- Local exhaust ventilation
- Natural ventilation techniques
- Avoiding air quality compromises
- Managing humidity to improve indoor air quality
- Understanding the impact of EWI on condensation
- Active humidity control
- Ventilation and moisture management
- Regular monitoring and inspection
- Lifestyle considerations
- Building maintenance
- Mitigating chemical pollutants
- EWI's impact on improved indoor air quality
- Enhanced temperature stability and reduced draughts
- Lower risk of mould and dampness
- Improved filtration and ventilation
- Energy efficiency and reduced emissions
- Enhanced acoustic insulation
- Long-term structural protection
- Incorporating plants for air purification
- HVAC system maintenance
In the hustle and bustle of daily life, we often overlook the importance of the air quality in our homes. Indoor air quality can significantly impact our health, well-being, and comfort. Poor air quality indoors can lead to a variety of health issues, including allergies, respiratory problems, and even long-term health effects. Fortunately, there are several steps you can take to improve the indoor air quality in your home. External wall insulation also significantly affects factors like ventilation, humidity, and the presence of chemical pollutants in your home.
Ventilation strategies
In homes with external wall insulation, the reduced natural airflow can lead to stale indoor air and potential accumulation of pollutants. Enhanced ventilation strategies become essential to maintain a healthy living environment.
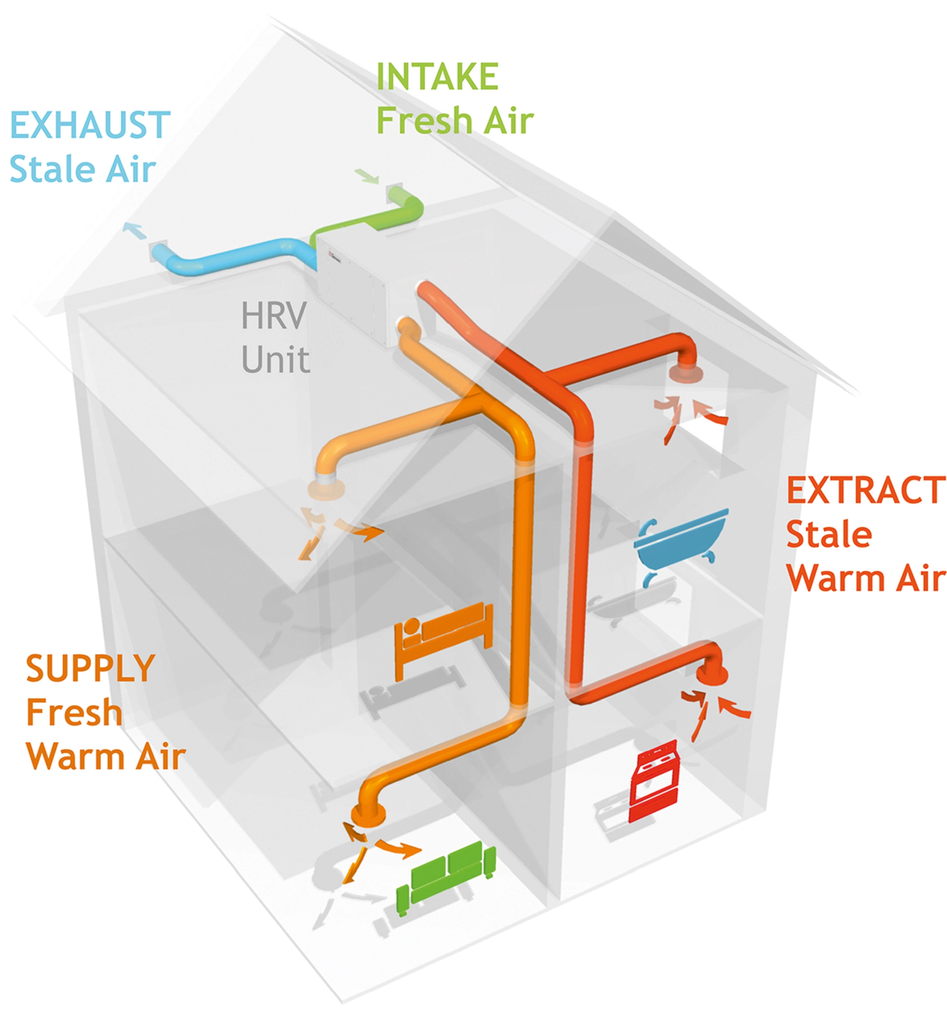
Mechanical ventilation systems
- Heat Recovery Ventilators (HRV) and Energy Recovery Ventilators (ERV): These systems are particularly effective in insulated homes. HRVs and ERVs not only provide a constant influx of fresh air but also retain most of the energy from the outgoing air. This means you can ventilate your home without losing much of the heat or coolness, maintaining energy efficiency.
- Balanced Ventilation: Ensure that your mechanical ventilation system is balanced, meaning it brings in as much fresh air as it expels stale air. This balance is crucial in maintaining an optimal indoor environment and preventing issues like negative air pressure.
Smart ventilation controls
- Automated Sensors: Modern ventilation systems can be equipped with sensors that monitor air quality, humidity levels, and CO2 concentrations. These sensors can automatically adjust the ventilation rates, ensuring optimal air quality at all times.
- Programmable Ventilation: Consider systems that allow you to program ventilation rates based on your daily routines, reducing energy usage when the house is empty and increasing it when the home is occupied.
Local exhaust ventilation
- Kitchen and Bathroom Fans: In areas prone to high humidity and odours, such as kitchens and bathrooms, use exhaust fans to remove excess moisture and cooking fumes. These fans should vent directly outside, not into attics or crawl spaces.
- Regular Maintenance: Keep exhaust fans clean and free of dust or grease build-up to ensure they operate efficiently.
Natural ventilation techniques
- Strategic Window Opening: While mechanical systems are effective, also take advantage of natural ventilation. Opening windows, especially in areas not covered by the insulation, can enhance air exchange. Cross-ventilation, where windows across a room or house are opened, can significantly improve airflow.
- Window Types and Placement: Consider the types of windows and their placement for optimal natural ventilation. For example, operable skylights can be effective in creating an upward draft, aiding in natural ventilation.
Avoiding air quality compromises
- Insulation and Sealing Checks: Regularly inspect your insulation and sealing around windows and doors to ensure there are no unintended gaps or leaks, which can compromise both your insulation’s effectiveness and indoor air quality.
- Education and Awareness: Be aware of the sources of indoor air pollution, such as cooking, cleaning products, and off-gassing from new furniture or building materials. Understanding these sources can help you manage indoor air quality more effectively.
Managing humidity to improve indoor air quality
External Wall Insulation (EWI) can significantly improve a building's thermal performance, often leading to a reduction in condensation within the home. However, managing humidity remains crucial to ensure a healthy indoor environment.
Understanding the impact of EWI on condensation
- Reduced Condensation Risk: EWI helps in maintaining a more consistent internal temperature across wall surfaces, reducing the likelihood of condensation which occurs when warm, moist air meets a cold surface.
- Improved Building Envelope: By creating a more airtight environment, EWI minimises the cold spots on walls that can lead to condensation and subsequent mould growth.
Active humidity control
- Use of Dehumidifiers: In areas prone to high humidity, such as bathrooms or kitchens, a dehumidifier can help maintain comfortable humidity levels, ideally between 30-50%.
- Smart Humidity Sensors: Modern dehumidifiers and HVAC systems with integrated humidity sensors can automatically adjust settings to maintain optimal indoor humidity.
Ventilation and moisture management
- Effective Ventilation: Even with reduced condensation risk, adequate ventilation is key to preventing moisture buildup. Utilise mechanical ventilation, such as HRVs or ERVs, to regulate indoor air moisture levels.
- Exhaust Fans in High-Moisture Areas: Ensure that bathrooms, kitchens, and laundry rooms are equipped with exhaust fans to expel moist air directly outside.
Regular monitoring and inspection
- Moisture Detection: Regularly inspect your home for signs of excess moisture, such as condensation on windows, peeling paint, or musty odours. Addressing these signs early can prevent more significant humidity problems.
- Thermal Imaging Inspections: Consider periodic thermal imaging inspections to check for insulation efficiency and potential moisture issues within walls.
Lifestyle considerations
- Indoor Plant Management: While indoor plants improve air quality, overwatering can increase indoor humidity. Ensure plants are watered appropriately and that pots have proper drainage.
- Mindful Activities: Be conscious of activities that generate a lot of moisture, like cooking, showering, or drying clothes indoors. Utilise lids on pots while cooking and avoid drying large amounts of laundry indoors.
Building maintenance
- Check for Leaks and Dampness: Regularly inspect the exterior and interior of your home for leaks or damp areas, particularly after heavy rain or snow. Addressing leaks promptly can prevent moisture from seeping into the structure.
- Gutter and Drainage Maintenance: Ensure that gutters and drainage systems are clean and functioning correctly to direct water away from the building, reducing the risk of moisture ingress.
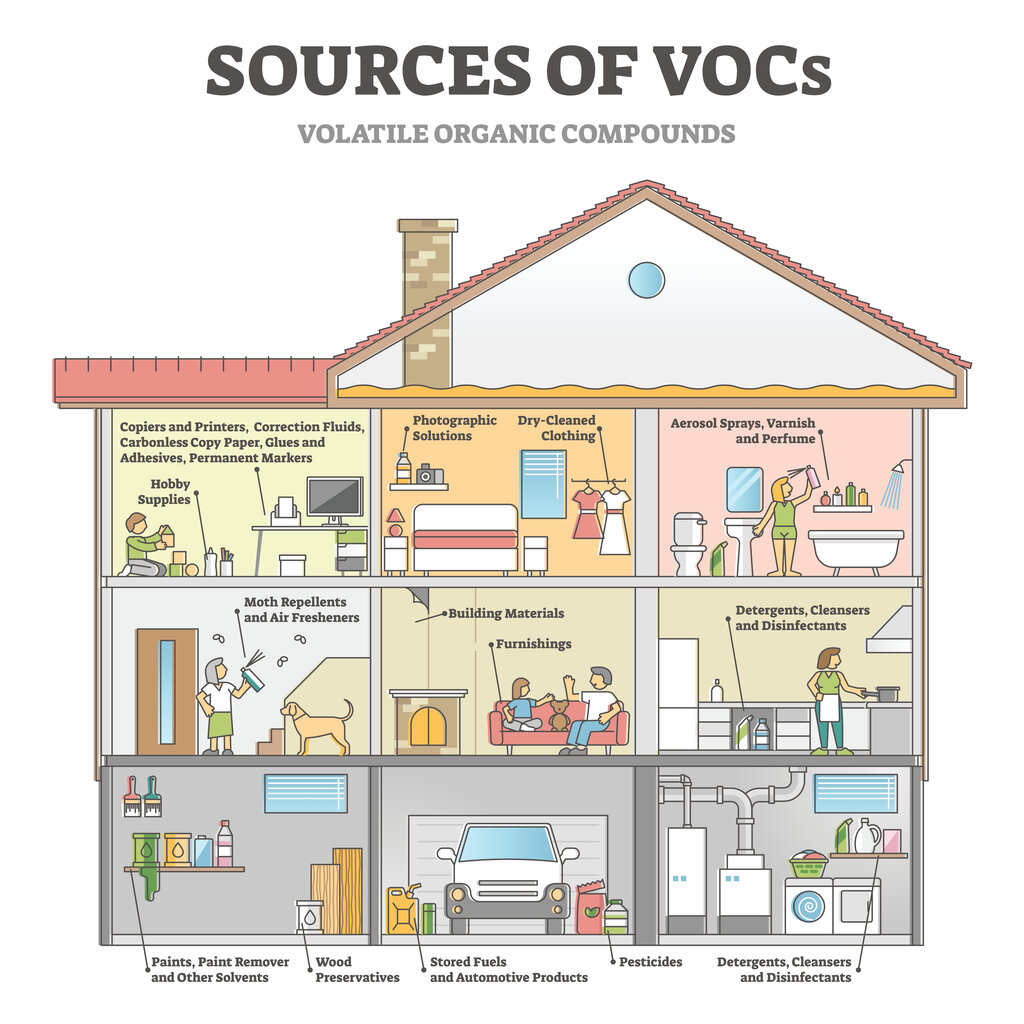
Mitigating chemical pollutants
While external wall insulation itself might not emit VOCs, other building materials and household items can.
- Low-VOC Interior Materials: Choose paints, furnishings, and flooring with low or no VOC emissions to minimise indoor air pollution.
- Natural Cleaning Products: Use natural or homemade cleaning solutions to reduce the chemical load in your indoor air.
- Indoor Air Quality Monitors: Consider using an indoor air quality monitor to detect and manage levels of VOCs and other pollutants.
EWI's impact on improved indoor air quality
Enhanced temperature stability and reduced draughts
- Stable Indoor Climate: EWI creates a thermal barrier, leading to a more stable indoor temperature. This stability reduces the likelihood of conditions that can lead to dampness and mould growth, which are common indoor air pollutants.
- Minimised Cold Draughts: By eliminating cold spots and draughts, EWI reduces the movement of dust and allergens within the home. This is especially beneficial for individuals with allergies or respiratory issues.
Lower risk of mould and dampness
- Prevention of Condensation: EWI increases the surface temperature of internal walls, significantly reducing the risk of condensation, which is a primary cause of mould growth. Mould spores are known to deteriorate indoor air quality and can pose health risks.
- Moisture Management: With EWI, homes become more airtight, which, when coupled with effective ventilation systems, allows for better control of moisture levels inside the house.
Improved filtration and ventilation
- Enhanced Ventilation Systems: In well-insulated homes, the use of mechanical ventilation systems (like HRVs or ERVs) becomes more common. These systems not only provide a constant supply of fresh air but also include filters that remove pollutants from incoming air.
- Reduced Infiltration of Outdoor Pollutants: EWI can decrease the infiltration of external pollutants such as pollen, traffic fumes, and industrial pollutants, by sealing potential entry points.
Energy efficiency and reduced emissions
- Lower Heating and Cooling Requirements: By improving thermal efficiency, EWI reduces the need for excessive heating or cooling, which can contribute to indoor air pollution if heating systems are not well-maintained or if they burn fossil fuels.
- Reduced Carbon Footprint: The energy efficiency gained from EWI also means lower carbon emissions associated with heating and cooling, contributing to overall better air quality both inside and outside the home.
Enhanced acoustic insulation
- Noise Reduction: EWI can also improve the acoustic insulation of your home, creating a quieter indoor environment. This might not directly affect the chemical composition of the air, but a reduction in noise pollution is an important aspect of overall environmental quality in the home.
Long-term structural protection
- Building Longevity: By protecting external walls from the elements, EWI can prolong the life of the building materials, reducing the likelihood of material degradation that can release particles or chemicals into the indoor air over time.
Incorporating plants for air purification
Indoor plants can play a role in absorbing indoor pollutants and improving air quality.
- Selection of Air-Purifying Plants: Include plants like spider plants, snake plants, and peace lilies which are known to absorb toxins.
- Avoid Overwatering: Ensure plants are not overwatered to prevent mould growth in the soil.
HVAC system maintenance
Regular maintenance of HVAC systems is crucial, especially in homes with external wall insulation.
- Regular Filter Replacement: Change filters as recommended to ensure efficient operation.
- Air Duct Cleaning: Clean air ducts to prevent dust and mould accumulation, which can be circulated by the HVAC system.
