
The amount of energy saved by insulation varies depending on several factors, including the type of insulation used, the climate of the area, the type of heating and cooling system in the home, and the part of the house that's insulated. However, it's clear that insulation can make a substantial difference in a home's energy usage.
How to measure energy
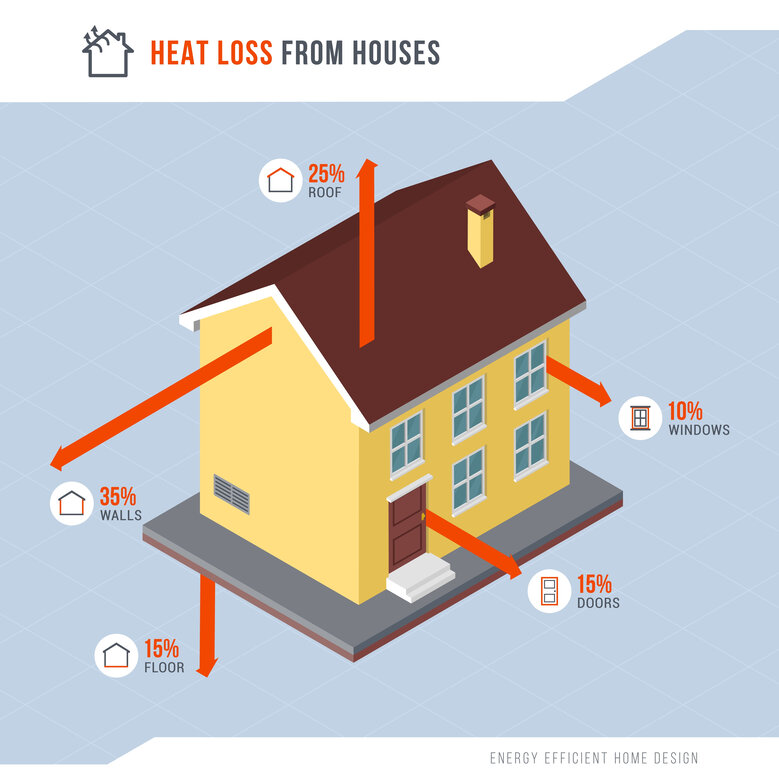
Energy use in the home is typically measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh). A kilowatt-hour is a unit of energy that equates to one kilowatt (1 kW) of power being used for one hour. On your utility bills, your energy use will generally be calculated in kWh. When it comes to energy loss in homes, heat energy is usually the main concern. Heat loss occurs when the warm air inside your house escapes to the outside, or when cold outside air infiltrates your home. The exact amount of heat loss can depend on many factors, including the size and shape of your home, the type and amount of insulation, and the efficiency of your heating system. However, here are some typical percentages for how heat is lost in a home that doesn't have any insulation:
- Windows and Doors: Around 15-20% of heat is lost through windows and doors, particularly if they're single-glazed or if there are gaps that allow draughts to come in. Therefore, air tightness goes hand in hand with insulation. Double or triple-glazing makes a significant impact on energy saving.
- Walls: Around 25-35% of heat is lost through uninsulated walls. For homes with solid walls, the figure can be even higher, as solid walls allow twice as much heat to escape as cavity walls do.
- Roof: Around 25% of heat is lost through the roof in an uninsulated home.
- Floors and Draughts: Around 15-25% of heat loss occurs through floors and as a result of draughts.
- Ventilation: Around 5-10% of heat is lost through ventilation systems.
How much energy does insulation save?
According to the U.S. Department of Energy, homeowners can typically save up to 15% on heating and cooling costs (or up to 10% on total energy costs) by air sealing their homes and adding insulation in attics, floors over crawl spaces, and accessible basement rim joists. The UK Government and independent regulators do not offer such figures. Therefore, this blog utilises the figures supplied by the US department. Whilst, in theory, the heat loss percentages will be similar, the UK will have specific issues, especially with pre-1920s solid wall housing stock. However, the figures paint a solid illustration of where heat is lost. These figures are only estimates. The actual energy savings will depend on the specific characteristics of the home, the occupants' lifestyle, the type of heating system, and fuel prices. But insulation will almost always reduce energy consumption, making homes more comfortable and reducing their carbon footprint. The U-value of an insulation material, which measures how well it resists heat transfer, is a key factor in determining its energy-saving potential. Lower U-values indicate better insulation properties, which means greater energy efficiency. So, while it's hard to give a precise figure without knowing the specifics of a given situation, it's safe to say that adding insulation is likely to result in significant energy savings. Investing in high-quality insulation with a low U-value can lead to even greater savings over time. In terms of environmental impact, insulation reduces the amount of energy needed to heat and cool homes. This reduces the amount of harmful greenhouse gases released into the atmosphere. So, not only does insulation save energy and money, but it also contributes to the fight against climate change.
Specific figures for how much energy insulation saves
Quantifying the precise savings of each form of insulation can be challenging due to the variety of factors that impact energy usage. These include climate, the building's size and design, the type of heating and cooling systems used, and the occupants' habits. However, the U.S. Department of Energy provides some estimates based on national averages that give a sense of the potential savings each type of insulation can offer:
- Blown-in Cellulose Insulation: This common attic insulation can save homeowners 20-50% on their energy bills.
- Fibreglass Batts: When properly installed, fibreglass insulation in the attic can reduce heating and cooling costs by approximately 10-15%.
- Spray Foam Insulation: This is more efficient than traditional methods of insulation, potentially saving homeowners up to 20% on heating and cooling costs. For some, the savings can reach up to 40%.
- Rigid Foam Insulation: This type of insulation, often used for basements and exterior walls, can reduce energy costs by up to 20%.
- Reflective or Radiant Barrier: This type of insulation, typically installed in attics in hot climates, can reduce cooling costs by 5-10%.
- Mineral Wool Insulation: This type of insulation can reduce energy costs by up to 15%.
It's important to remember that these numbers are just estimates. Energy savings depend on a wide range of factors and may vary significantly from one household to another. Always consider your unique circumstances. Also, consult with an insulation professional to get the most accurate understanding of potential energy savings for your specific situation.
The UK and energy savings
While the UK government bodies, such as the Energy Saving Trust, don't provide exact savings percentages for each type of insulation like the U.S. Department of Energy, they do provide some approximate annual savings figures.
- Loft Insulation: If all homes in the UK install 270mm of loft insulation, it could save up to £135 per year.
- Cavity Wall Insulation: Cavity wall insulation can save up to £150 per year.
- External Wall Insulation: If you live in a home with solid walls, 45% of your heat is escaping through the walls which is costing you money. By insulating your solid walls, you could save in excess of £500 a year if you live in a detached house.
- Floor Insulation: Proper floor insulation can save approximately £25-£65 per year.
- Insulating a Hot Water Cylinder: This could save around £115-£150 per year.
As always, it's important to remember that these are estimated figures based on average-sized gas-heated homes in the UK. Actual savings will vary depending on the size and age of your home, the number of occupants, and how efficiently you use energy.
